Unveiling Iran On The World Map: A Deep Dive Into Its Geography & History
Exploring the vast and ancient land of Iran on the world map reveals a country of profound historical significance, diverse geography, and immense cultural richness. Often at the crossroads of global attention, understanding Iran's physical location, its borders, and its internal landscape is crucial to appreciating its past, present, and future. This article aims to provide a comprehensive look at Iran's geographical footprint, its key features, and its place in the broader global context, drawing on various facts and figures to paint a complete picture.
From its strategic position bridging the Middle East and South Asia to its bustling capital city, Tehran, Iran offers a captivating blend of ancient heritage and modern complexities. Whether you're interested in its majestic mountains, sprawling deserts, or vibrant cities, an in-depth exploration of the Iran map world is an essential first step. Let's embark on a journey to uncover everything you want to know about this fascinating nation.
Table of Contents
- Persepolis Iran
- News Iran War
- Famous People From Allentown Pa
- Iran Latest Military News Today
- Lizzie Mcguire The Movie Cast
- 1. Iran's Strategic Location on the World Map
- 2. Unpacking Iran's Diverse Geography
- 3. Borders and Neighboring Countries: A Geopolitical Nexus
- 4. Iran in Numbers: Size and Population Compared
- 5. Vibrant Cities and Provinces: The Heartbeat of Iran
- 6. A Tapestry of History and Culture: From Persia to Iran
- 7. Economy and Natural Resources: Powering the Nation
- 8. The Geopolitical Landscape: Iran's Role on the World Stage
1. Iran's Strategic Location on the World Map
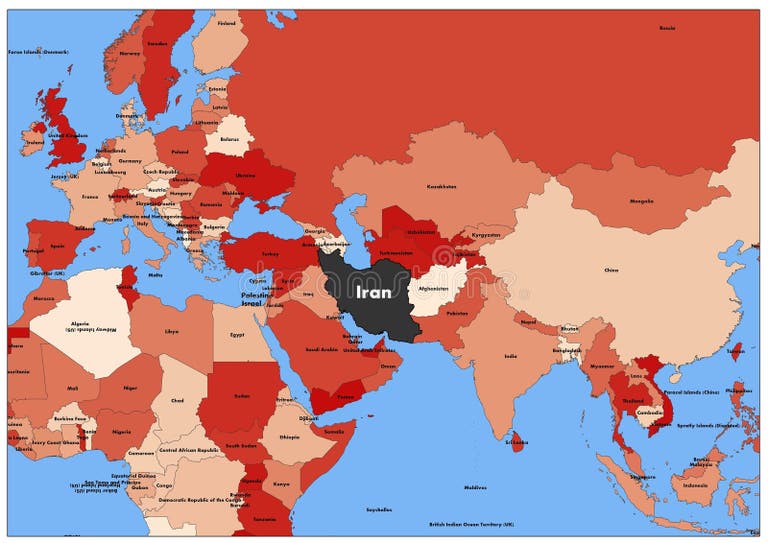
When you locate Iran on the world map, its strategic importance immediately becomes apparent. Situated in Southwestern Asia, Iran occupies a critical position, bridging the Middle East and South Asia. This central location has historically made it a hub for trade, cultural exchange, and geopolitical influence throughout its long history. The nation's unique placement gives it access to vital waterways and land routes, shaping its development and interactions with surrounding regions and the world.
Specifically, Iran lies between the Caspian Sea to the north and the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman to the south. This dual access to major bodies of water is a defining feature of its geography, providing significant economic and strategic advantages. The country's coordinates place it roughly between latitudes 24° and 40° N, and longitudes 44° and 64° E, firmly anchoring it within the Northern Hemisphere and the Eastern Hemisphere. This position on the Iran map world is not merely geographical; it dictates its climate, its historical trade routes, and its contemporary geopolitical role.
2. Unpacking Iran's Diverse Geography
The geography of Iran is remarkably diverse, encompassing a wide array of landscapes from towering mountain ranges to vast deserts and fertile coastal plains. This topographical variety is a key aspect to explore when looking at the Iran map. The country is largely dominated by the Iranian Plateau, with various mountain ranges forming natural barriers and defining distinct regions. The Zagros Mountains, running from the northwest to the southeast, are the largest mountain range, while the Alborz Mountains, in the north, contain Mount Damavand, the highest peak in Iran and the Middle East.
Beyond the mountains, Iran is home to two major deserts: the Dasht-e Kavir (Great Salt Desert) and the Dasht-e Lut (Empty Desert). These arid regions cover a significant portion of the central and eastern parts of the country, presenting unique environmental challenges and opportunities. Despite the prevalence of deserts, Iran also boasts fertile plains, particularly along the Caspian Sea coast, which benefit from a humid, subtropical climate, starkly contrasting with the arid interior.
2.1 Mountains, Deserts, and Coasts: Natural Wonders
Understanding Iran's natural wonders through its geography helps to appreciate the country's resilience and beauty. The mountains are not just geographical features; they are crucial for water resources, providing snowmelt that feeds rivers and sustains agriculture in lower elevations. They also offer stunning landscapes for tourism and provide habitats for diverse wildlife.
- Mountains: The Alborz range, home to Mount Damavand (5,610 meters or 18,406 feet), and the extensive Zagros range are vital for Iran's climate and water supply.
- Deserts: The Dasht-e Kavir and Dasht-e Lut are among the hottest and driest places on Earth, showcasing extreme natural beauty and unique geological formations. The Lut Desert, in particular, is a UNESCO World Heritage site known for its "kaluts" (yardangs), massive corrugated ridges formed by wind erosion.
- Coasts: Iran has significant coastlines along the Caspian Sea to the north and the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman to the south. These coasts are important for trade, fishing, and host vibrant port cities. The northern coast has a lush, green landscape, while the southern coasts are more arid but boast rich marine biodiversity and strategic islands.
This varied topography influences everything from climate zones and agricultural practices to population distribution and infrastructure development across the Iran map.
3. Borders and Neighboring Countries: A Geopolitical Nexus
Iran shares extensive land and sea borders with numerous countries, solidifying its role as a geopolitical nexus in the region. Its borders extend for more than 2,000 kilometers (1,200 miles), including nearly 650 kilometers (400 miles) of coastline along the Caspian Sea. The land borders connect Iran to a diverse set of neighbors, each with its own historical and contemporary relationship with Tehran.
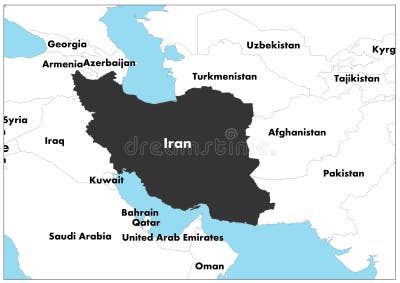
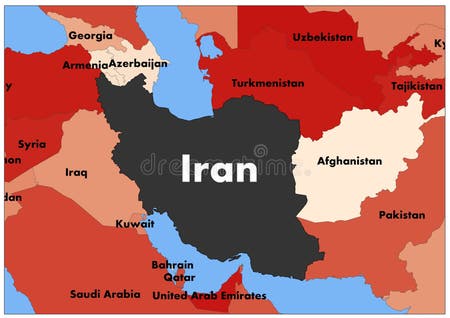
To the west, Iran borders Iraq and Turkey. To the northwest, it shares borders with Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Turkmenistan. To the east, its neighbors are Afghanistan and Pakistan. These borders are not merely lines on an Iran map; they represent historical trade routes, cultural exchanges, and, at times, areas of geopolitical tension. The long border with Afghanistan, for instance, is significant for migration and trade, while the borders with Iraq and Turkey have been historically crucial for regional stability and economic ties.
The maritime borders in the Persian Gulf and Gulf of Oman are equally vital. These waters are among the most important oil shipping lanes in the world, making Iran's control over its coastline a matter of global economic and strategic interest. The proximity to countries like Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Qatar, Bahrain, and the UAE across the Persian Gulf further highlights Iran's central role in the Middle East's energy landscape and regional dynamics.
4. Iran in Numbers: Size and Population Compared
To truly grasp the scale of Iran, it's helpful to look at its size and population in comparison to other countries. With an area of 1,648,195 square kilometers (636,372 sq mi), Iran ranks seventeenth in size among the countries of the world. This makes it a considerably large nation, comparable to the combined size of France, Germany, Spain, and the United Kingdom.
In terms of population, Iran is also a significant global player. It is the 17th most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 85 million people. In the Middle East, it's one of the most populated nations, often cited as the third most populated after Egypt and Turkey in the broader region. This large and relatively young population contributes to a dynamic workforce and a substantial domestic market, influencing its economic trajectory and social development.
A quick comparison on the Iran map with other nations highlights its substantial footprint. For instance, comparing Israel vs. Iran on a map immediately shows a vast difference: Iran is much, much bigger than Israel, around 75 times larger, and also has significantly more people. This disparity in size and demographics is a fundamental factor in regional power dynamics and strategic considerations.
5. Vibrant Cities and Provinces: The Heartbeat of Iran
Iran is home to several vibrant and culturally rich cities that showcase its historical and contemporary significance. These urban centers, spread across its numerous provinces and districts, are the economic, political, and cultural heartbeats of the nation. Exploring the Iran map through its cities offers a glimpse into its diverse heritage and modern life.
The country is divided into 31 provinces (ostanha), each with its own capital city and unique characteristics. These provinces vary widely in terms of geography, climate, population density, and cultural traditions. From the ancient cities with their stunning Islamic architecture to modern metropolises, Iran's urban landscape is a testament to its long and continuous civilization.
Some of the most famous travel destinations and attractions are found within these cities:
- Isfahan: Known for its stunning Islamic architecture, including Naqsh-e Jahan Square (a UNESCO World Heritage site), Imam Mosque, and Sheikh Lotfollah Mosque.
- Shiraz: The city of poets, gardens, and nightingales, home to the tombs of Hafez and Saadi, and close to the ancient ruins of Persepolis.
- Yazd: A desert city with unique traditional architecture, windcatchers, and a strong Zoroastrian heritage.
- Tabriz: A historical city in the northwest, famous for its Grand Bazaar (another UNESCO site) and its role in the Iranian Constitutional Revolution.
- Mashhad: The holiest city in Iran, home to the Imam Reza Shrine, a major pilgrimage site for Shia Muslims.
These cities, along with countless smaller towns and villages, form the intricate network of human settlement that defines the Iran map, each contributing to the nation's rich tapestry.
5.1 Tehran: The Bustling Capital
The capital city, Tehran, is a bustling metropolis that serves as the center of the economic and political map of Iran. Located at the foot of the Alborz Mountains, Tehran is Iran's largest city and one of the largest cities in Western Asia. It is a vibrant hub of culture, commerce, and innovation, reflecting the modern face of the nation while still preserving elements of its rich history.
Tehran's location offers a unique blend of urban development and natural beauty, with ski resorts just a short drive away in the mountains. As the political capital, it houses government institutions, foreign embassies, and the offices of major national and international organizations. Economically, Tehran is the primary industrial and financial center of Iran, attracting people from across the country seeking opportunities.
The city's cultural scene is equally dynamic, with numerous museums, art galleries, theaters, and parks. From the Grand Bazaar to modern shopping malls, and from ancient palaces like Golestan Palace (a UNESCO site) to contemporary architectural marvels, Tehran offers a microcosm of Iran's diverse offerings. Its strategic position on the Iran map, combined with its massive population and economic power, makes it an undeniable force in the country's development.
6. A Tapestry of History and Culture: From Persia to Iran
Iran boasts one of the world's oldest continuous major civilizations, with historical and cultural roots stretching back thousands of years. Its history is a rich tapestry woven with the rise and fall of empires, the flourishing of arts and sciences, and profound spiritual developments. Learning about Iran's history, culture, religion, and politics from various sources provides a deeper appreciation of this ancient land.
The country's cultural heritage is evident in its magnificent architecture, exquisite Persian carpets, classical poetry, and diverse culinary traditions. Persian, or Farsi, is the official language, spoken by the majority of the population, though various regional languages and dialects also exist. Islam, specifically Shia Islam, is the official religion, deeply influencing the nation's laws, social norms, and cultural expressions.
Throughout its history, Iran has been a cradle of innovation, contributing significantly to mathematics, astronomy, medicine, philosophy, and literature. Figures like Avicenna, Rumi, and Omar Khayyam are celebrated globally for their contributions, reflecting the intellectual prowess that has long been a hallmark of Persian civilization. The cultural influence of Iran extends far beyond its borders, impacting regions from Central Asia to the Indian subcontinent.
6.1 From Persia to Iran: A Name's Evolution
One of the frequently asked questions about the country is why Iran changed its name from Persia. While the Western world predominantly referred to the country as Persia for centuries, the native people had always called it Iran. The name "Iran" derives from "Aryanam," meaning "Land of the Aryans," referring to the ancient Indo-Iranian tribes who settled in the region. The term "Persia" comes from the ancient Greek name for the region, "Persis," which in turn referred to the province of Fars (Persis in Greek), where the Achaemenid Persian Empire originated.
In 1935, Reza Shah Pahlavi officially requested that the international community use the native name "Iran" instead of "Persia." This decision was part of a broader nationalist movement aimed at asserting Iran's distinct identity and its ancient heritage, moving away from a name that was seen as an exonym and associated primarily with one province rather than the entire nation. While "Persian" is still used to refer to the language, culture, and certain historical aspects, "Iran" is the official name of the country on the world map and in international relations.
7. Economy and Natural Resources: Powering the Nation
Iran's economy is largely driven by its vast natural resources, particularly oil and natural gas, making it a key player in the global energy market. The country holds the world's fourth-largest proven crude oil reserves and the world's second-largest natural gas reserves. These resources are fundamental to its economy, influencing its GDP, trade balance, and geopolitical standing.
Beyond hydrocarbons, Iran possesses significant reserves of other minerals, including iron ore, copper, zinc, lead, and coal. The mining sector, while not as dominant as oil and gas, contributes to the national economy and offers potential for diversification. Agriculture also plays an important role, with a variety of crops grown across its diverse climate zones, from wheat and rice to fruits and nuts, including the world-renowned saffron and pistachios.
Despite its rich natural endowments, Iran's economy has faced challenges, including international sanctions, which have impacted its ability to fully leverage its resources and integrate into the global economy. However, the country has also pursued policies of economic diversification, investing in non-oil sectors such as petrochemicals, automotive manufacturing, and tourism. Understanding these economic facets provides a fuller picture of the modern Iran map and its aspirations.
8. The Geopolitical Landscape: Iran's Role on the World Stage
Iran's strategic position in the Middle East and its significant natural resources mean it plays a pivotal, and often complex, role on the world stage. Its geopolitical landscape is shaped by its regional relationships, its nuclear program, and its interactions with major global powers. The country's actions and policies often have ripple effects across the Middle East and beyond, making it a constant subject of international discourse.
Iran's strategic location, bridging the Middle East and South Asia, makes it a critical actor in regional stability. Its borders with countries like Iraq, Turkey, Afghanistan, and Pakistan, combined with its access to the Persian Gulf, underscore its influence on trade routes, energy security, and regional conflicts. The ongoing developments concerning its nuclear program, for instance, are a significant aspect of its foreign policy and a major point of discussion in international relations.
8.1 Regional Dynamics and Global Implications
The regional dynamics involving Iran are multifaceted. Its relationships with neighboring countries, as well as with global powers, are constantly evolving. The Persian Gulf, bordered by Iran to the north, is a critical waterway for global oil shipments, making any tensions in the region a matter of international concern. Iran's role in various regional conflicts, its support for different non-state actors, and its missile capabilities are all factors that contribute to its complex geopolitical profile.
The "Data Kalimat" mentions instances of conflict, such as "Israel launched a series of strikes against Iran, targeting the country’s nuclear program and other military infrastructure, Iran launched its own strikes in retaliation," and "Israel began pounding Iran on June 13, in a conflict that has the world holding its breath because of fears it could rapidly escalate and drag Britain and the US in." These events highlight the sensitive and often volatile nature of regional relations. While this article focuses on the geographical and factual aspects of the Iran map world, it's impossible to ignore the geopolitical context that shapes perceptions and interactions with the country. These dynamics underscore why understanding the precise location and features of the Iran map is not just an academic exercise but a practical necessity for comprehending global affairs.
Conclusion
From its strategic location on the world map, bridging diverse regions and cultures, to its rich tapestry of history, geography, and vibrant cities, Iran is a nation of immense depth and significance. We've explored its vast size, its considerable population, its diverse natural landscapes from the towering Alborz mountains to the arid Dasht-e Lut deserts, and its vital access to both the Caspian Sea and the Persian Gulf. We've also touched upon its historical transformation from Persia to Iran and the dynamic geopolitical role it plays in the modern world.
Understanding the Iran map world is not just about pinpointing a country on a globe; it's about appreciating a civilization that has shaped human history, continues to influence global affairs, and offers a wealth of cultural and natural wonders. We hope this comprehensive guide has provided you with valuable insights into this fascinating country. What aspects of Iran's geography or history do you find most intriguing? Share your thoughts in the comments below, and consider exploring more of our articles to deepen your knowledge of global geography and culture!
- Ben And Jerrys Ice Cream
- Thomas Peterffy Wife
- Will Isreal Attack Iran
- Melanie Griffith Dating
- Who Is Leader Of Iran
Iran World Black Map Random Background Classic Style Stock Illustration
Iran World Black Map White Background Classic Style Stock Illustration
Iran World Black Map Random Background Classic Style Stock Illustration